Turn Customer Data into Valuable Insights and Improved Operations with Customer 360
- Blog >
- Turn Customer Data into Valuable Insights and Improved Operations with Customer 360

Your customers generate a lot of data. There’s a wealth of information in this data if you can understand the relationships between that data, leading enterprise organizations to implement customer 360 initiatives.
Customer data – across a wide spectrum of industries, from retail to insurance to health care and beyond – comes in many forms, including purchase history, social media, search activity, support calls, customer reviews and feedback, patient information, etc.
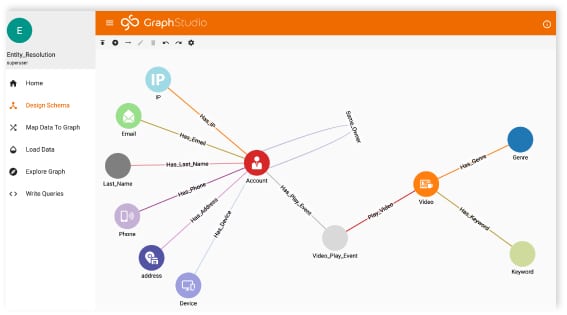
Customer 360 is the ability to get a holistic view of your customer data, in all its forms and wherever it resides. Having a 360-degree view of your customers means you can gain valuable insights that improve your customers’ experience while also improving profitability.
In a recent Graph + AI Summit presentation, Connected Data for a 360 View of Customers, Mark Thomas of Dell Technologies, and Scott Heath of Expero, explored the data challenges mega organizations face as well as the methods, graph technology included, companies such as top banks and major healthcare providers use to find insights within their customers’ data and improve overall operations.
Impediments to Customer 360
Every company wants to understand its customers better. For enterprise organizations, there are many reasons this is challenging.
- Continuing to use their historical approach, like relying on legacy systems and traditional technology
- Massive data sets
- Multiple types of data
Let’s look at that first sticking point, and how databases play a role.
Databases house customer data. Storing and accessing this data alone, however, is not enough, especially when it comes to analytics. Here’s a quick overview of three types of databases:
- Relational databases: Rigid schema structure, time-consuming queries, and poor performance for deep analytics.
- NoSQL databases: Flexibility to change the schema and offers horizontal scaling, but require long lead times for deep queries – they just weren’t built for transactional performance.
- Graph databases: More flexible than either relational or NoSQL databases and provide deeper analytics.
Relational databases have been the go-to for a long time, but they just aren’t cut out to provide the deep insights, on big data, in real-time required for effective customer 360. “You need a toolset that makes the relationship between the data the first-class citizen, which is where relational databases fall short and where graph databases are purpose-built,” stated Mark Thomas.
“When we talk about graph systems,” he continued, “we’re referring to the storage and retrieval of not only the entity but the relationship between those entities.”
Relationships within your data matter immensely. This brings us to a couple of other challenges enterprise organizations face – the size and diversity of data. Graph platforms, especially TigerGraph because it can scale up and out, excel when the data is immense and complex.
Real-world Examples of Customer 360
Customer 360 benefits most industries, including banking, retail, healthcare, and more. Let’s take a look at how graph enables insights in real life in some of the most complex scenarios.
Healthcare
Improving patient experience by reducing the call center time was the goal of UnitedHealth Group, a multinational managed healthcare and insurance company. By using TigerGraph on-premises with Dell Technologies servers and AMD compute, “we demonstrated an improvement in patient record retrieval 10x better than goal, reducing query times from minutes to seconds,” said Mark. This was achieved despite an enormous amount of member data.
Why does this matter? A shorter call time obviously improves the patient experience. It also improves both the efficiency of the call center’s staff and the net promoter scores.
“All of this collectively drove down operating expenses.” Mark Thomas
Banking
Financial institutions utilize graph for detecting fraud. A bank can also use TigerGraph to identify customers at risk of leaving, known as churn, and then to ask the question: What is the impact of losing this individual? It’s logical the bank wants to know this information, but answering this type of question historically hasn’t been easy because seeing the relationships within the data sometimes wasn’t even possible.
By running TigerGraph analytics, the bank sees that this high net worth individual is connected to many other individuals in the same income bracket and has a sphere of influence. By losing him, the bank may lose multiple accounts. Therefore, the impact of losing a particular high net worth individual is much greater than losing just one account holder. Knowing this, the bank can take proactive steps to minimize churn.
To learn more about graph technology, how graph helps Dell.com, UnitedHealth Group, and banks, and to see a customer 360 demo of TigerGraph capabilities, watch the full presentation.