Use Cases of Graph Databases in Automotive Applications
- Blog >
- Use Cases of Graph Databases in Automotive Applications
This article was originally published on Medium.com by Behzad Benam, IT Consultant & Architect at msg, on April 25, 2022, and is republished with permission.
TigerGraph offers efficient solutions for creating graph databases for applications in the automotive industry.
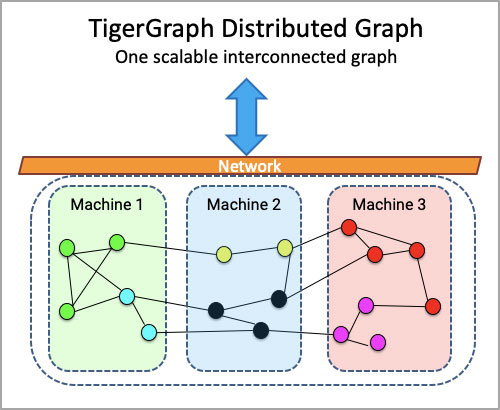
Getting the data representation right is a critical decision in any data-driven project. The graph type of data representation was initially used as a recommendation by Netflix, Google, Linkedin, and Amazon. Compared to relational databases with tables connected by primary and foreign keys, we have nodes and edges connecting nodes and defining relationships in a graph database.
We usually use query languages to access data in a database. In relational databases, we often use SQL as the query language. A graph database is a NoSQL database, and data access is supported by query languages such as Cypher, GraphQL, Gremlin, AQL, or SPARQL. Below, I will present use cases from the automotive industry that are likely to be applicable in other sectors. The aim is to show that the automotive industry can take advantage of graph databases and take more significant steps toward digitizing the industry much faster.
Product Management
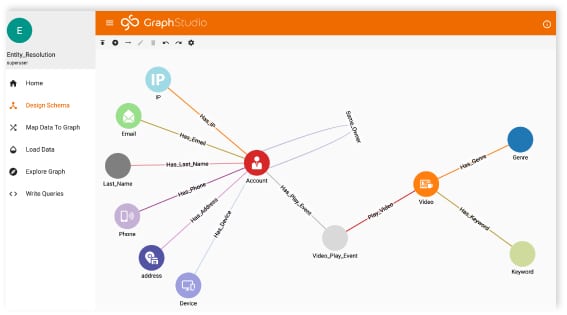
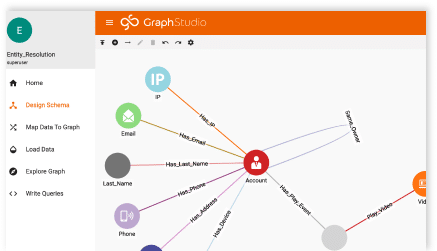
Product management as a primary category includes three use cases: production, sales/after-sales, and supply chain management. The exciting point about implementing the graph databases is that you can create each graph database separately and then connect them via new relationships to get a more extensive data model of the system as a whole.
Separating graph databases of all system elements reduces complexity in the earlier database design process. After designing each graph database, we can connect all graph databases by finding the right nodes and adding the required relationships.
Production Management
Product and supplier-related data are the most significant nodes in the production management graph database. A product has a production process that includes multiple components delivered by a supplier. A product has documentation and a manual. The production receives the product order from the sales organization and checks the technical availability such as hardware and software components and test routines. The system will notify the customer when the production order is complete.
Sales and After-sales Management
The sales organization, customer, and product are the most influential data in this graph database. Customers can request the purchase, repair of the product, or maintenance. The customer could also ask for information about the product or even request a resale, which the original retailer could likely handle.
Supply Chain Management
Suppliers should deliver a bug-free product and test it in advance. The vehicle production team should schedule and synchronize all testing required for a supplier’s product at vehicle production. All test results should be stored in a documentation database to be accessible to the customer service team.
System Safety
Safety mechanisms should avoid unacceptable risks resulting in product behavior. One aspect is functional safety considering random hardware failures and systematic failures. Another aspect of safety is looking at it from an operational perspective and what could go wrong in a given scenario or which scenarios are still unknown to designers. We can show that graph databases can be applied to both safety aspects. Typically, a safety analysis based on hardware failures in functional safety and trigger events in the safety of the intended function (SOTIF) is performed to derive overarching safety requirements or goals.
Functional Safety: Component Reliability and Safety
System components and properties are the central nodes in the graph database for functional safety analysis. The vehicle condition can change positively depending on strategic, tactical, or operational tasks and negatively due to component malfunctions. Safety measures can make the system stable again. These events are a part of relationships and properties between two different system components. The Fault-Tolerant Time Interval (FTTI) can be viewed as relationship property, whether we can achieve it or not.
Safety of Intended Function (SOTIF)
The basis of SOTIF analysis could be similar to functional safety analysis but using different data, relationships, and safety mechanisms. The functional components are the central nodes in the graph database for SOTIF analysis. The vehicle status can be changed positively depending on strategic, tactical, or operational tasks and negatively by triggering events in the corresponding driving scenarios.
Safety measures can make the system stable again if a functional component violates a safety goal. The “triggering events” are not hardware component failures and are all events or functional component failures that harm the vehicle’s driving behavior. An example could be a pedestrian or cyclist suddenly appearing in front of a car. Each new undesired event can make the system unstable and requires a dedicated safety mechanism to bring the system into a safe state.
System Security
Automotive security should ensure the integrity, authenticity, confidentiality, and availability of the system. There are different levels of security analysis in automotive applications. The first level is the embedded level. An attacker will attempt to access the embedded hardware communication buses, such as the CAN bus, to manipulate memory or an actuator value. The second security aspect is on the cloud side or in the vehicle control center. The third aspect is the communication between vehicles and infrastructure or backend.
Depending on which level of security analysis is our objective, we should take the central nodes. For example, we should consider hardware or functional components at the embedded level. We usually consider a machine (Windows, Mac, etc.) as an element of IT security, and users and their permissions are the nodes and relationships.
The goal is not only to know who is gaining illegal access to the vehicle but also to design a robust system architecture and security mechanisms against possible attacks. All data communicated between the vehicle and infrastructure or backend can affect the vehicle status from a security point of view. It could also be a negative impact emanating from an attacker in any state. A security mechanism can be modeled as a relationship to make the system stable again after an attack.
Summary
A graph database is a general approach to representing data efficiently. We can benefit more from this approach when the system is very complex, and there is a large amount of system data interacting with each other, and they have complex relationships. A fundamental step in creating a graph database is what part of the data is taken as a node and how relationships relate to those nodes.
When making this decision, we must consider system elements, stakeholders, possible use cases, and scenarios. The goal should be to create a database of the whole system and show all interactions between system elements and stakeholders in different use cases and scenarios from the point of view of the analysis goal. Graph databases allow us to model the entire system and understand all interactions between all stakeholders.
We can reduce the risks of the system by modeling a single risk analysis graph for all possible risks, including safety and security. Graph databases help us visualize the entire system, analyze, detect, and mitigate all potential hazards or threats in real-time, and ultimately recover the system and protect all assets. The application of machine learning is an added value to keep systems up to date against cyber attacks in the next step.