Anti-Money Laundering Analytics with Graph DB
Detect Money Laundering With TigerGraph

Money Laundering Is Costing the Economy Billions
Money laundering and financial fraud is a problem that has become even harder to track with the proliferation of real-time digital transfers and payments, complex international laws and the rise of cryptocurrencies. The United Nations Office of Drug and Crime estimates that money laundering is 2-5% of global GDP (or $800 billion-$2 trillion). Governments across the world have increased regulatory oversight to stop money laundering to the extent that a 2018 survey from LexisNexis estimated that the cost of regulatory compliance for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) for U.S. financial services firms now exceeds $25 billion annually.

Legacy Approaches to Detecting Money Laundering Are Insufficient
Virtually all existing anti-money laundering analytics compliance systems are built upon relational databases, which store information (customer, account, transaction, etc.) in rows and columns. Relational databases are great tools for indexing and searching for data, as well as for supporting transactions and performing basic statistical analysis. These are, however, poorly suited to connecting dots and identifying hidden relationships, which is essential for analyzing money trails and assessing their money laundering risk. Such queries could take hours or even days to run, rendering any meaningful analysis of linkages among parties and transactions practically impossible.
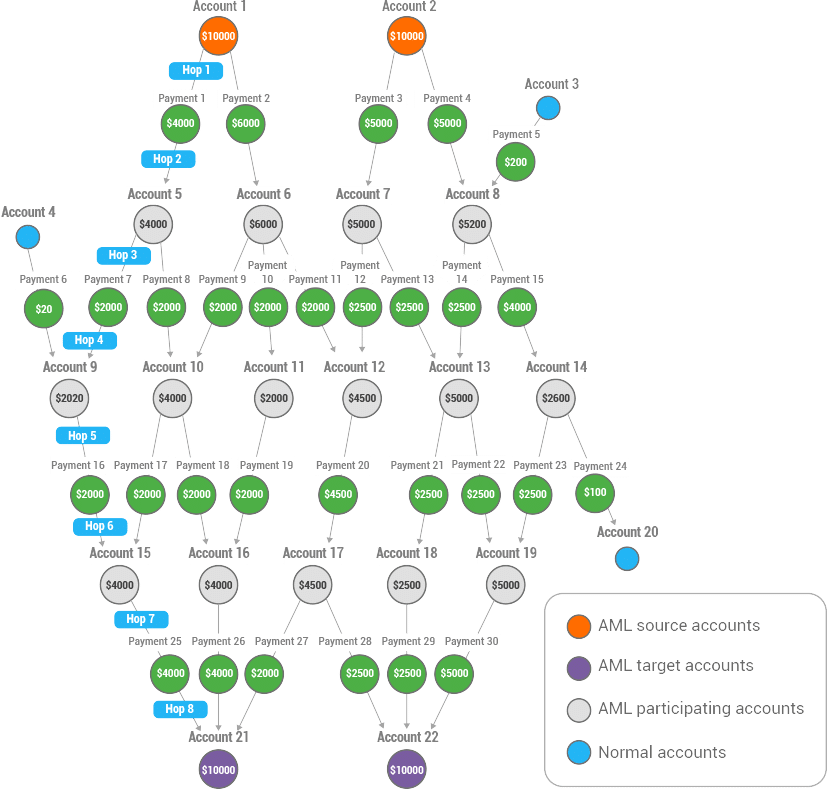
Detecting money laundering and financial fraud requires going beyond individual account behavior, analyzing relationships among groups of accounts or entities over time often combining information from third party sources. Traditional money laundering solutions built on relational databases were not designed to address this challenge.
Why TigerGraph, a Native Parallel Graph Database for AML?
Reduce False Positives With Deep Link Analytics
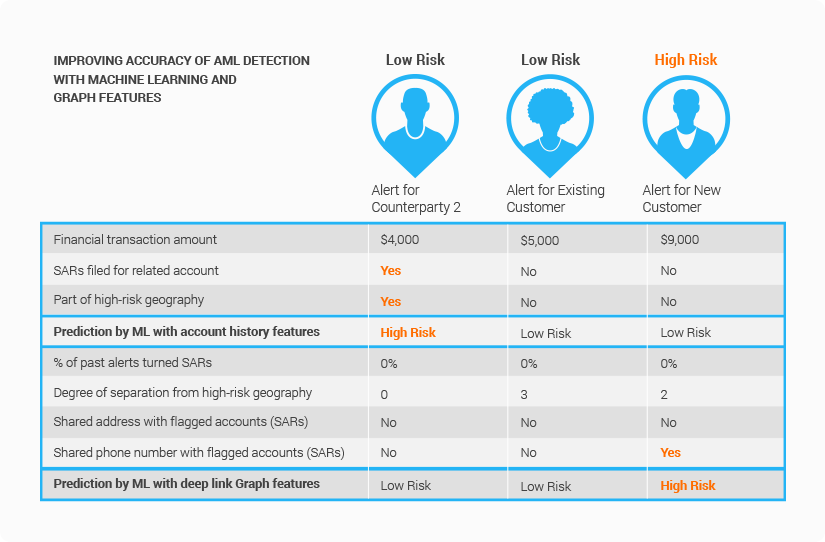
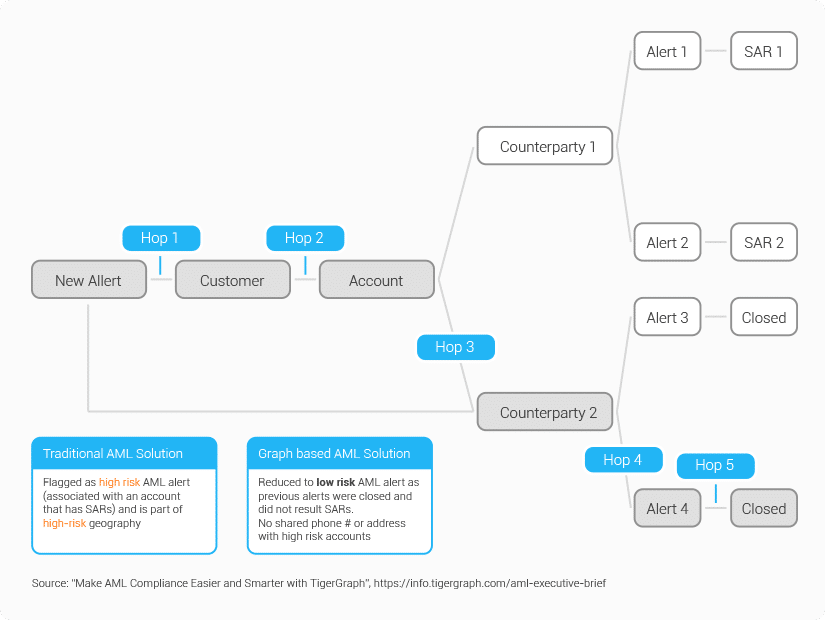
Approximately 95% of the money laundering alerts raised with legacy systems are unrelated to money laundering. Consider the example, where a new alert was raised for a counterparty, Counterparty 2 that has had recent financial transactions with a customer account linked to Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). Traditional approaches would suggest that this new alert is high risk, because the traditional metrics, such as a high number of alerts generated and multiple SARs filed on the same customer account, all point to the likelihood of high AML risk.
Nonetheless, through graph analysis, it turns out that of all the previous alerts, only those related to Counterparty 1 became SARs while those related to Counterparty 2 have all been closed. Given that this new alert is related to Counterparty 2, it will likely be more similar with alerts 3 and 4, as opposed to alerts 1 and 2, and thus probably should be closed, or at least marked as low risk. TigerGraph’s deep link analytics can identify and group “like” alerts where a conventional transaction monitoring system would miss the relationship.
Graph Analytics Can Reduce False Negatives in Money Laundering Detection
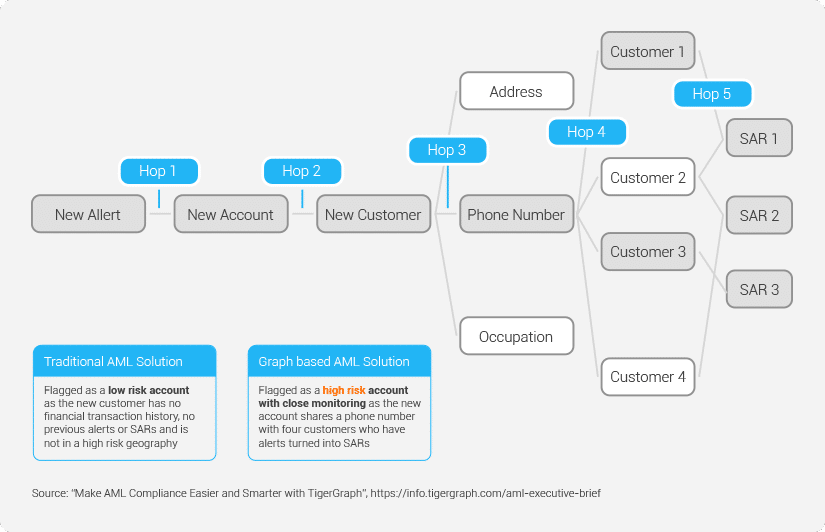
Money launderers typically create an intricate network of identities and accounts to funnel their ill-gotten gains. This makes it particularly hard and time-consuming to find the false negatives buried deep inside the mountain of legitimate transactions. Consider the example where a new customer account is added. The new customer account is marked as a low-risk account under a conventional scoring approach, because none of the other attributes measured by the traditional scoring model such as high-risk geography, transaction amount or number of previous alerts or SARs display significant money laundering risk.
However, the conventional approach fails to consider the cluster of high-risk customers who have an undeclared relationship with the new customer. The new customer shares a phone number with four other existing customers who have multiple SARs and are therefore designated as high risk. Such hidden or undeclared relationships through a phone number would have been quite difficult to uncover using human review or existing models and systems. TigerGraph’s deep link analytics reveals the hidden relationship in real-time and elevates the new alert to a high-risk alert.
Machine Learning Improves the Accuracy of Money Laundering Detection
Machine learning has been integrated by multiple financial service providers with their existing anti-money laundering solutions. However, the accuracy for AML detection is quite poor, as the traditional solutions generate a lot of false positive alerts, feeding those as training data into artificial intelligence. This, in turn, affects the accuracy for predicting AML activity.
Consider the three alerts described in the example. Let’s look at how the alerts were rated based on traditional features based on account history and how they are classified based on graph-based relationship features computed by TigerGraph.
Training data from traditional AML solutions for machine learning includes features such as financial transaction amount, SARs filed for the related account and if the particular account is part of a high-risk geography. Based on these features, an alert is raised for Counterparty 2 as Counterparty 2 has received funds from a customer account that is also doing business with Counterparty 1 and there are SARs filed for Counterparty 1 based on past transaction history. Counterparty 2 is also in a high-risk geography.
After reviewing features generated by TigerGraph, the alert for the Counterparty 2 is reduced to low risk – all alerts in the past for this account have been closed and none have converted into SARs. Even though the account is in high-risk geography, it does not share phone, address or any other information with a high-risk account with SARs. Graph-based features have essentially ruled out a false positive in the AML alert for Counterparty 2. Let’s consider the alert for the new customer, who is not located in high-risk geography, does not have any alerts or SARs as they do not yet have a history with the financial institution.
Traditional AML systems will not flag an alert for the new customer – graph-based features, however, dig deeper and find that the new account shares a phone number with several customers with SARs: a graph solution creates a new AML alert that was missed by traditional AML solution and marks it as high risk for further monitoring and investigation. A graph solution identifies these false negatives.