Why Supply Chain Disruptions Are a Data Problem
- Blog >
- Why Supply Chain Disruptions Are a Data Problem
This article was originally published at The New Stack here on April 5, 2022.
A butterfly flaps its wings in Tokyo and weeks later a hurricane hits the coast of California. This, of course, is the oversimplified metaphor that describes the oft-quoted “Butterfly Effect,” which suggests that a minor event can have a major impact on a complex system. To put in the context of our current state, when a container ship gets stuck in the Suez Canal, supply chains around the globe suddenly seize up.
But here’s the point that seems to get lost amidst all the talk about supply chain vulnerabilities: There is nothing “unexpected” about supply chain disruptions. They are inevitable, varying only in the degree or magnitude of disruption. The real problem lies in our inability to plan for and respond to these disruptions. So-called “black swan”-type events that lay outside the margins of conventional forecasting models wreak havoc on interdependent systems such as supply chains. This is especially true now in a world of just-in-time manufacturing — an environment in which keeping excess inventory on hand is strongly discouraged.
What worldwide events such as COVID-19 and Brexit have demonstrated is that these events themselves have little to do with a supplier’s ability to produce a part. Rather, it’s the uncertainty that these events introduce into the planning calculus that can prompt chaos throughout an entire supply chain. One need look no further than what’s currently happening in the market for new cars. When the COVID-19 pandemic took hold in early 2020, auto manufacturers made what seemed like a calculated bet by cutting their orders for semiconductor chips as they anticipated the demand for new vehicles would slump amidst an environment of economic uncertainty. These chips were then snapped up by other industries for other uses, including phones, computers, and video games. The global semiconductor shortage has put the brakes on worldwide auto production. A single part is unavailable, and production of the entire vehicle is stalled. Production in some factories is at a complete standstill. In fact, auto inventory levels are down 64% compared to last year. As trade wars, materials shortages, and natural events fuel further disruption, the traditional way of managing supply chain risk (by calculating a minimum inventory buffer) will be ineffective given the wildly unpredictable swings in supply.
The Constraints of Relational Databases
Even before COVID-19, most enterprises recognized the need to have more granular visibility across not just their own suppliers but all the suppliers further upstream. However, gaining this visibility across multiple tiers — and being able to map all of these relationships in real time — requires a new approach.
This is due in large part to the limitations of traditional relational databases that most companies still rely on to manage and track thousands of suppliers, the parts they produce, and the myriad dependencies that exist among them. Relational databases store data for each business entity such as customer, order, product, and payment information in separate tables. In order to understand and analyze relationships across various entities, relational databases require table joins, which can take hours to perform and become computationally intensive as the volume of data grows in size. Meanwhile, managing these long chains of relationships using traditional enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems becomes problematic since the underlying architecture isn’t optimized for modeling relationships and dependencies.
Relational databases were primarily designed for steady data retention rather than rapid scalability. So while they are well-suited for managing certain static data types and processes, these databases are unable to meet the demands of today’s dynamic, data-intensive applications and use cases. These demands include delays in the delivery of critical components, unplanned logistics costs, assembly lines in certain regions sitting idle, and more. Companies have gigabytes (or terabytes) of relevant supply chain data, but it’s spread throughout the organization.
Graphing the Future Supply Chain
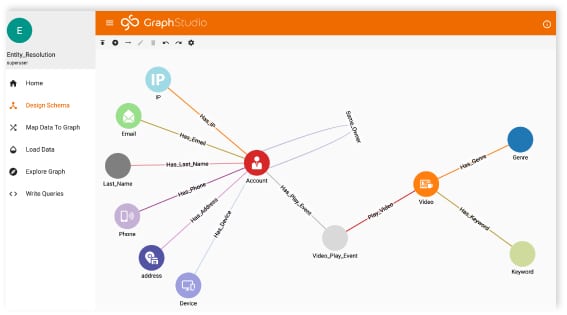
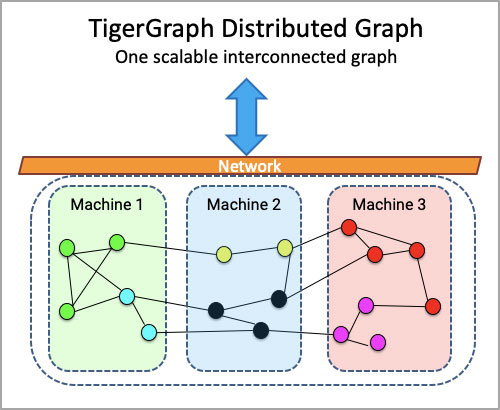
A graph database builds on the mathematical theory of graphs, which represents data as a network of nodes (what you know) and edges (how it’s connected). Unlike a relational database, which is slower and unable to uncover real-time relationship patterns, a modern graph database can model disparate relationships and dependencies in a way that closely mirrors the real world. A modern graph database should be able to load massive amounts of data in hours and analyze extended chains of relationships — all in real-time.
Graph also delivers a “what-if” engine, allowing companies to create a digital representation of a system or process (such as an automotive supply chain). Teams can then run models to predict changes in supply or consumer behavior based on complex, interdependent, and dynamic data. In this way, the graph represents a “digital twin” of your real-life supply chain, and as such, it serves as a framework that can both house all your data and visualize the relationship between disparate data types. Most importantly, graph representations of supply chain data can be used to make specific alternative plans in response to global changes in supply and demand. If you can’t build what you planned because a part is unavailable, what can you build now with what you do have?
The building blocks of supply chain management include strategic planning, demand planning, supply planning, operations management, logistics, manufacturing, warehousing, procurement, and transportation — each of which is a specialized function in its own right. Graph databases are ideal for organizing and visualizing this data as an integrated whole. What’s more, graph analytics provides the tools to ask deep and complex questions that aim to understand not only the individual data points, but the relationships among all the cooperating links that exist in the supply chain.
Graph algorithms such as shortest path, geographical proximity, and object connectedness can uncover previously hidden relationships that can help manage and mitigate complex dependencies in real-time. Many internal and external factors (involving parts, people, and things) simply cannot be anticipated, and businesses must be on standby for the unpredictable. They must be ready to tackle product resequencing to next-best products, process monitoring, end-to-end impact analysis resulting from any change, supplier constraint, commitment management, and more.
What makes modern graph databases of particular value is that they don’t require specialized data experts to build and run queries. Instead, they are designed to be used by the same non-technical business users who manage the supply chain. These users can then identify, understand, and resolve system and data-related issues quickly — and this saves time, reduces cost, and controls risk (as much as possible, anyway).
As we have witnessed over the past two years, there’s a multiplier effect at work with supply chain inefficiency — it’s not just the hard costs that must be considered, it’s also the impact that it has on forecasting. Disruptive events like the pandemic have simply magnified the risks that were already present in the system and made them more apparent. The sooner we can appreciate the fact that modern supply chains are a data problem that require a modern approach, the better prepared we will be for the next global disruption — whatever that might be.